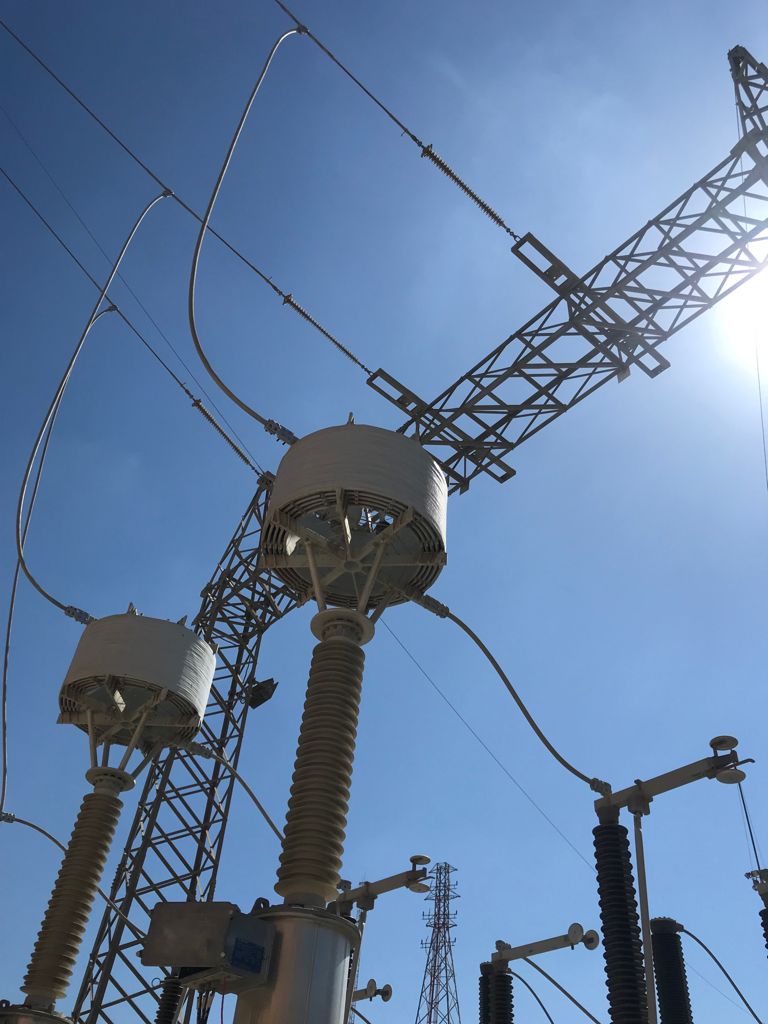
Line Traps are essential components utilized in transmission and distribution networks. Power Line Carriers (PLC) play a crucial role in power transmission systems, while facilitating remote control signals, voice communication and remote metering and control between substations within the electrical transmission and distribution networks.
Features
- Standards: IEC 60353, IEEE Std. C93.4, IEEE Std.643
- Manufactured according to specified short circuit requirements
- Light weight design facilitates easy mounting
- Cooling spacers contribute to lower winding temperatures that reduce the temperature of the windings
- Tuning unit box can be easily replaced without dismantling the coil when frequency adjustments are needed
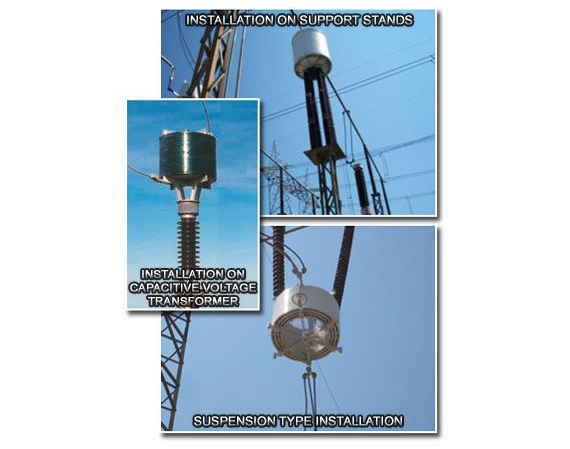
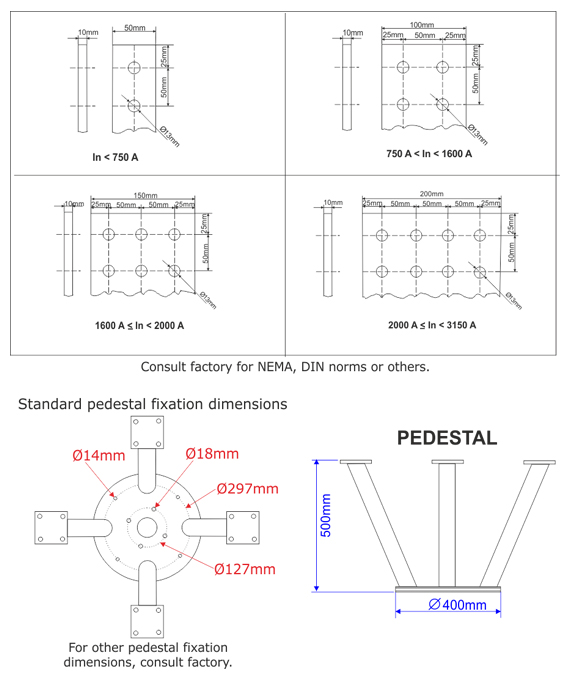
- Suitable for installation on capacitive voltage transformers, supports, insulators or suspension mounts
- Low stray capacitance and high quality factor
- Corona spheres provided for voltages over 245 kV
- Accommodates various types of conductor terminals
- Available in DIN or NEMA type terminal configurations
Selection Details
- Inductance of Line Trap (mH)
- Nominal Current (A), at 50 or 60 Hz
- Short Circuit Current (kA) and duration
- Blocking frequency range (kHz)
- Network voltage (kV)
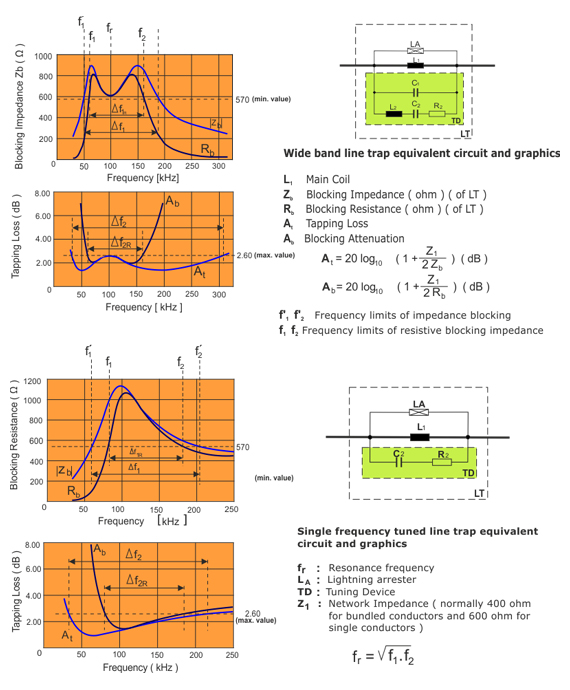
- Blocking impedance, Zb
- Resistive component of blocking impedance, Rb
- Capacitive voltage transformer mounting provision (pedestal) or suspension
- Connection terminal special requirements (DIN or NEMA)
- Bird barrier
| Nominal Current (A) | Standard Short Circuit Currents (kA/1 second) | Inductance (mH) |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | 10-16 | 0.10 / 0.20 / 0.315 / 0.4 / 0.50 / 1.00 / 2.00 |
| 630 | 16-20 | |
| 800 | 20-25 | |
| 1000 | 25-31.5 | |
| 1250 | 31.5-40 | |
| 1600 | 40-50 | |
| 2000 | 50-63 |
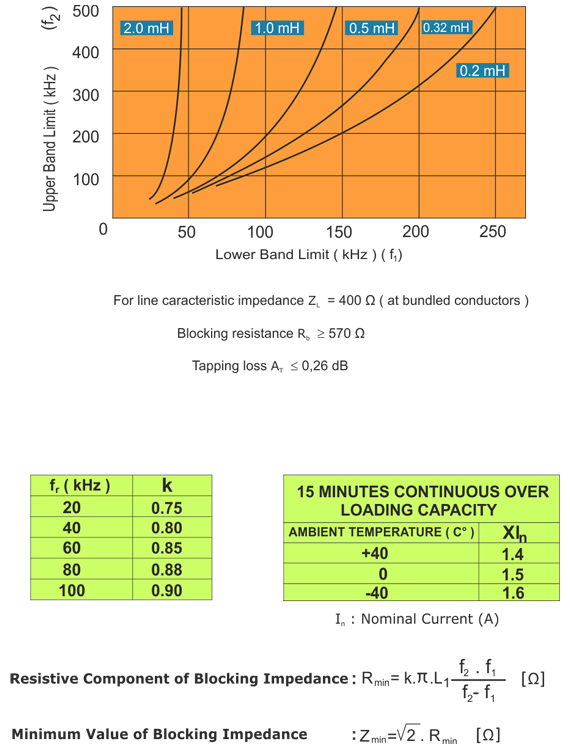
Blocking Bandwidths of Tuning Devices