The widespread use of nonlinear loads hinders the quality of electric power around the world. Some examples of this are power electronics-based equipment and electric arc & ladle melt furnaces. One of the most important parameters for defining the power quality is harmonic distortion.
The harmonic distortion in a network causes:
- Equipment heating
- Insulation failure due to overheating and higher voltage peaks than rated fundamental voltage (50Hz or 60Hz) sinusoidal signal
- Equipment malfunction (false zero cross detection on power electronics devices)
- Communication interference or noise
- Fuse and breaker mis-operation
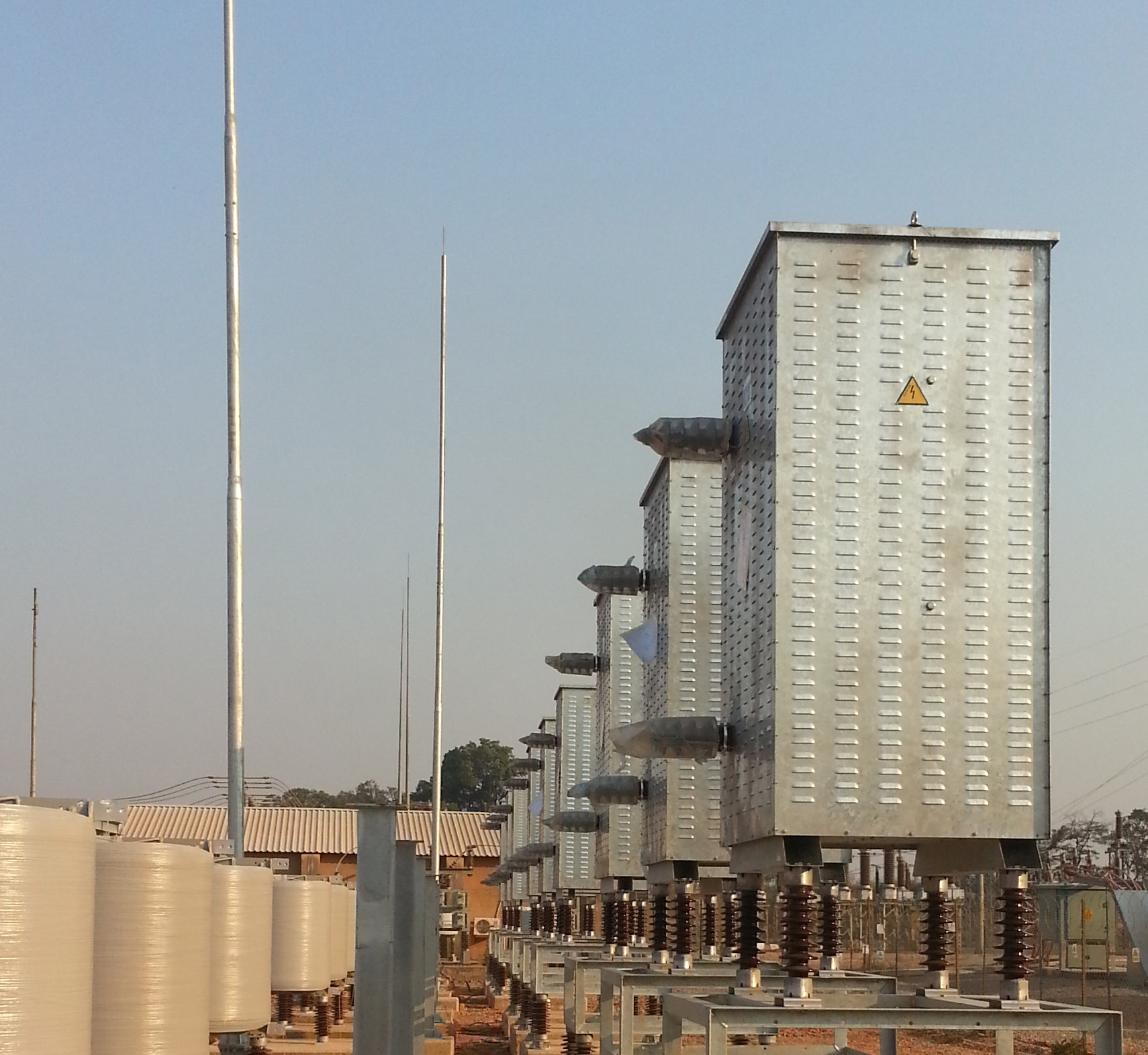
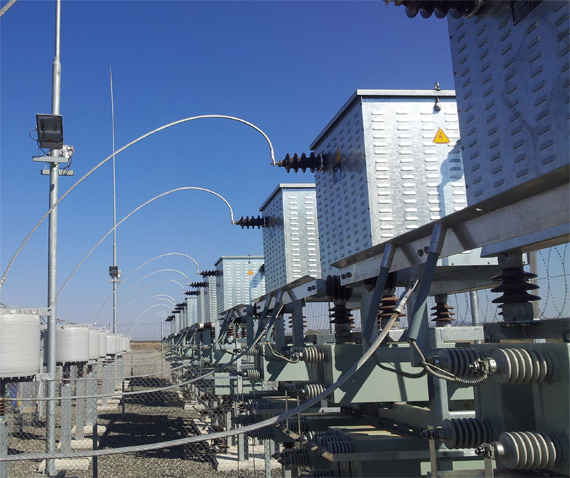
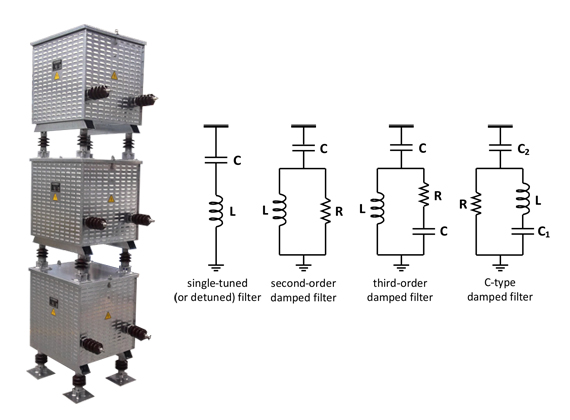
Passive harmonic filters are the most commonly used devices for reducing the harmonic distortion in a network. These filters are built up from passive RLC components, i.e. resistors, inductors and capacitors.
These resistors are used either to control the percentage of harmonics to be filtered and dissipate the heat corresponding to those harmonic currents, or to lower the risk of amplification due to parallel resonance problems.
The widespread use of nonlinear loads hinders the quality of electric power around the world. Some examples of this are power electronics-based equipment and electric arc & ladle melt furnaces.
Harmonic filter damping resistors may be used in single-tuned, second order, C-type and high-pass harmonic filters, according to the type of load and purpose.
| Technical Specification | |
|---|---|
| Voltage | Up to 36 kV |
| Altitude | Up to 1000 m * |
| Installation | Indoor / Outdoor |
| Resistance Material | Stainless steel alloy |
| Protection Degree | IP 23 (outdoor), others on demand |
| Temperature | -40°C to 55°C |
| Cooling | Air natural / Oil natural / Air forced |
| Options | Taps with DIN or NEMA terminal configuration |
*Consult factory for higher values.