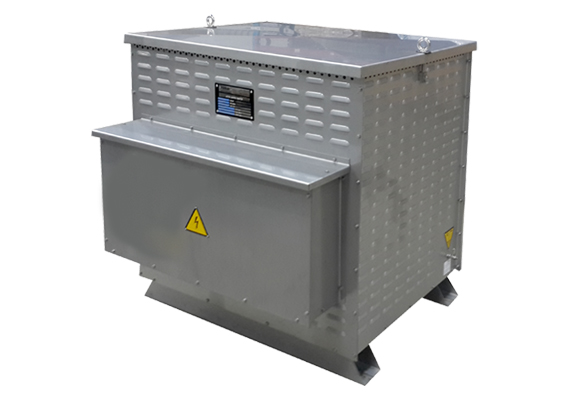
1. Stator Connected Resistors
Motor Starting Resistors are used to reduce the voltage at the motor terminals and also decrease the starting current.
Motor Starting Resistors are necessary because the self resistance of a motor armature is very low. When the voltage is first applied, excessive current will flow. Because there will be no back electromotive force (emf) to limit this current, some series resistance can be added to the armature windings.
As the motor accelerates, the back emf will build and the current through the resistor will thus decrease. Additionally, the voltage drop on the resistor will reduce, causing the voltage across the terminals increases. With this gradually increasing torque and voltage, the acceleration becomes smooth. The resistance is disconnected when the motor reaches a certain speed. At this point, the motor will run with full line voltage.
2. Rotor Connected Resistors
Rotor connected resistors are mainly used for motor starting applications which require a high-starting torque, such as loaded belt conveyors in the mining industry. By using external resistors, it is possible to shift the motor maximum (break-down) torque up to a starting torque point for motors under heavy loads during start-up. The resistors are split into steps and controlled via contactors by a motor starting control system. As the motor speed increases, the external rotor resistors are eliminated via shorting contactors until all external resistors are shorted out.
Area of Usage
- Overhead cranes
- Lift trucks
- Machine tools
- Conveyors
- Cement plants
- Industrial controls
- Steel mills
- Ships and submarines
- On load starting motors





