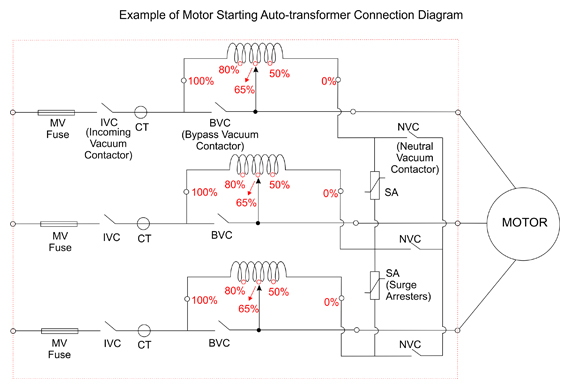
Motor Starting Auto-Transformers (MSA) serve to mitigate inrush current by decreasing the applied voltage during the start-up phase of both induction and synchronous motors.
Direct-online starting of a motor usually generates voltage flicker and mechanical stress to the equipment. To circumvent these issues, starting the motor at a reduced voltage is necessary a task accomplished through the use of an auto-transformer.
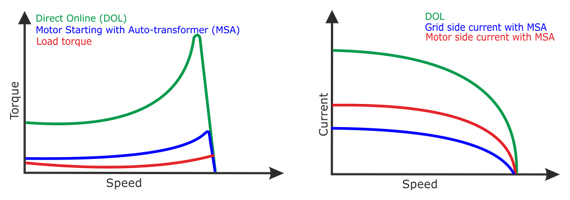
Auto-transformer significantly reduce the high starting current while providing moderate starting torque. They typically feature voltage taps set at 50%, 65% and 80% of the rated voltage. Unlike reactor-based motor starters where motor voltage remains fixed, autotransformers allow for further reduction in starting current while maintaining the same starting torque.
During the startup phase the motor is connected to the taps of the auto-transformers, resulting in lower starting voltage and consequently lower current draw, yielding less torque compared to connection to the line voltage.
Starting Characteristics
- Motor terminal voltage is less than line voltage (by transformer ratio)
- Motor current exceeds line current (by inverse of transformer ratio)
- Starting torque is reduced by the square of the motor terminal voltage